7 Differences between QLED and OLED Display Panels
You may have come across OLED display panels in malls or electronics stores, and they have grown in popularity since their introduction in televisions in 2007. OLED technology is also commonly used in other devices such as laptops and smartphones.
But what about QLED? Is it similar to OLED, or is it a different display technology? Don't let the differences confuse you. In this article, the Carisinyal team and I will explain the differences between QLED and OLED panels commonly used in televisions. Read on to understand the differences between these two technologies.
Differences Between QLED and OLED Panels
I have identified about seven differences between QLED and OLED panels, covering their materials, operating principles, and characteristics. Let's take a look at each one individually!
1. QLED Is LCD, OLED Doesn't Use LCD
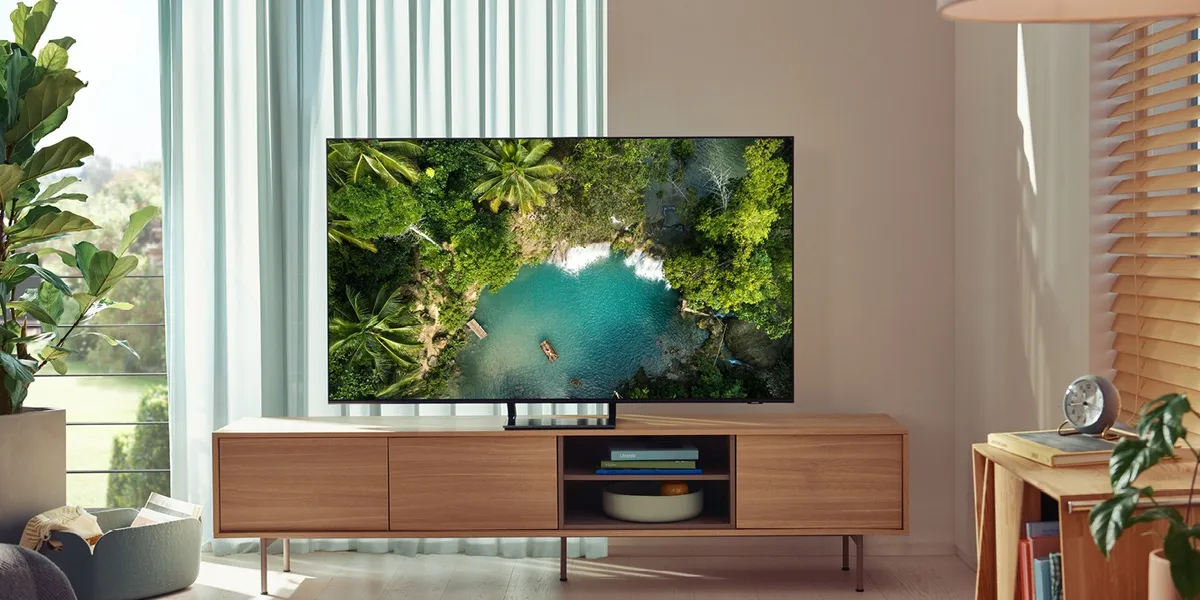

QLED is actually a term that Samsung popularized on a number of its TV product lines. They have been using this term since 2017. Even so, other TV manufacturers also use QLED technology, such as TCL.
The name QLED is taken from quantum dot + LED technology. Technically, QLED belongs to the TFT-LCD family, just like SVA, WVA, IPS, and PLS.
LCD panels are composed of several layers. There is a backlight lamp as a light source, a polarizer, LCD liquid crystals (pixel formers), color filters, and transistors.
In QLED panels, the backlight used is an LED lamp with blue light, just like other TFT-LCD panels. A quantum dot layer is installed between the backlight and the color filter. A quantum dot is a crystal-shaped semiconductor particle that is 2 to 10 nanometers in size. It contains green and red particles.
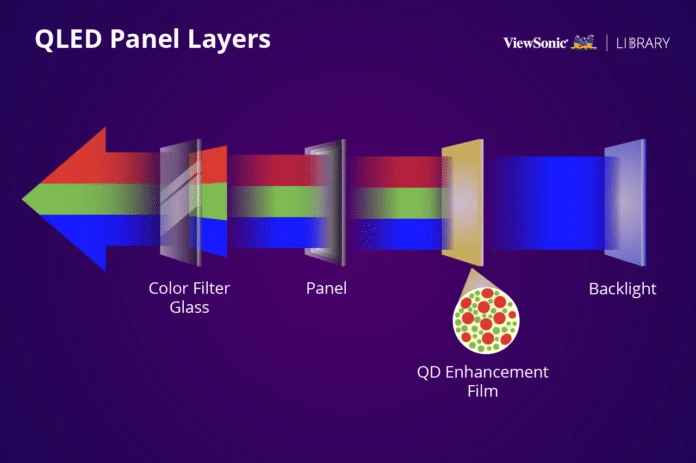
When the particles combine with blue light, they create a purer white light compared to standard white LED lights. This improves contrast, color accuracy, and brightness while increasing energy efficiency, reducing losses compared to other TFT-LCD displays.
This mechanism differs from other TFT-LCD panels such as IPS panels, where white light is generated by blue light passing through the yellow phosphor layer, resulting in less white light compared to QLED panels.
In short, QLED excels in color reproduction among LCD display panels, while OLED operates on a different principle. OLED does not require backlighting as it radiates light (emissive). OLED relies solely on filters to produce specific colors, and some OLED panels eliminate the need for color filters altogether.
OLED panels without filters feature blue, red, and green LEDs, while OLED panels with filters use white LEDs. TVs generally use OLEDs with filters, while smartphones often use OLEDs without filters.

OLED consists of fewer components than LCD. Besides the many LED lights, there is also a polarizer, which prevents reflection of external light to maintain screen visibility. OLED variations include P-OLED and AMOLED.
In 2022, a new OLED display panel variant emerged, known as QD-OLED. This panel combines OLED technology with a quantum dot layer, which replaces the color filter.
The main difference between QLED and QD-OLED lies in the function of the quantum dot layer. In QLED panels, this layer is used to create brighter white light.
On the other hand, in QD-OLED panels, the quantum dot layer is used to produce color. Samsung and Sony TVs are already using QD-OLED technology.
2. QLED is Thicker than OLED
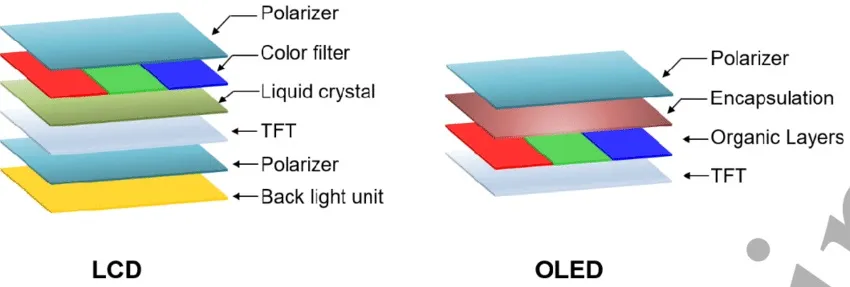
As mentioned earlier, QLEDs are categorized as TFT-LCD panels, resulting in a more complicated structure compared to OLED displays. This complexity entails more components needed to assemble a complete panel, which in turn leads to a thicker QLED profile.
According to Japanese display manufacturer Futaba, TFT LCD panels are typically between 5-15 mm thick, so QLEDs fall within this range. In contrast, OLED panels are thinner, ranging from 0.9-2.5 mm. In addition to its slim profile, OLED panels are also lighter compared to TFT-LCD panels.
As an illustrative example, let's consider two Samsung televisions-one featuring QLED technology and the other OLED. The 65-inch Samsung QLED 4K Q70B is 25.7 mm thick and weighs 21.4 kg.

Second, the 65-inch Samsung OLED 4K S95C is 11 mm thick and weighs 18.9 kg.

This comparison clearly shows that QLED televisions of the same size will consistently present a greater thickness and weight compared to OLED televisions.
3. Enhanced Color Contrast with OLED

The practical design of OLED display panels provides a vivid and pure color display, often described as bright. This characteristic is a natural strength of OLED technology, thus making it very popular for entertainment purposes such as gaming and HDR video playback. The contrast and dynamic range achieved by OLED displays are simply outstanding.
In contrast, TFT-LCD family display panels lag behind in this aspect. However, innovators continue to work towards bridging this gap, as evidenced by the emergence of quantum dot technology leading to QLED displays.
While QLED display panels offer impressive color contrast, they still fall short of OLED. OLED displays excel in producing absolute deep blacks, a feat that QLED has not been able to achieve, despite its advanced dimming technology. This difference arises from light leakage through the filter, resulting in slightly washed-out or slightly grayish blacks.
4. OLED Tends to be More Energy Efficient

On OLED display panels, producing black is just a simple matter of turning off certain pixels. This approach to producing black is different with QLED.
QLEDs and the entire LCD display family keep the backlight on no matter what color is displayed. When black is displayed, the filter prevents light from reaching the LCD crystal.
With this contrasting mechanism, it is clear that OLEDs generally offer greater energy efficiency compared to QLEDs. However, in the context of televisions, power consumption can also be affected by the various features integrated.
5. QLED Offers Superior Brightness, While OLED Excels in Viewing Angles
Most QLED and OLED televisions already provide good levels of brightness, especially when handling HDR content with dynamic range. However, when it comes to brightness, QLED has the upper hand.
Usually, QLED televisions achieve brightness levels ranging from 500 to 2000 nits. Specifically, the Samsung QN100B Neo QLED TV offers an impressive peak brightness of 5000 nits.
OLED televisions, on the other hand, offer brightness levels in the range of 500 to 1000 nits. Some of LG's OLED TVs equipped with META technology are reported to reach a brightness level of 2100 nits.
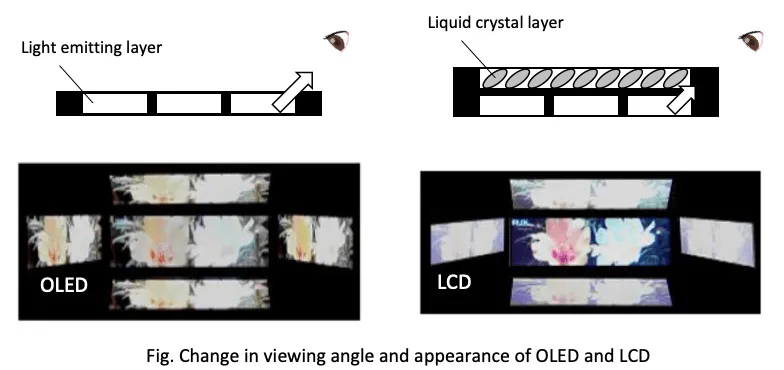
The higher brightness capability of QLED displays confirms the effectiveness of quantum dot technology, which shows its practicality is more than a gimmick. On the other hand, OLED outperforms QLED in terms of viewing angle.
Quantum dot technology has indeed contributed to improving the viewing angle, in addition to the brightness level and color gamut. However, some color shift can still occur when viewing the screen from different angles and distances, a limitation that does not exist with OLED display panels.
6. QLED Offers Longer Lifetime

Both QLED and OLED displays inevitably experience performance degradation over time, with the brightness of the screen gradually decreasing.
According to various sources, both QLED panel technologies are estimated to have a lifetime of up to 60,000 hours, while OLED panels typically last around 30,000 hours.
Assuming 3 hours of daily use, QLED televisions can last up to 54 years, while OLED televisions have a lifetime of about 27 years. Clearly, QLED displays show a longer lifespan compared to OLED.
This difference arises because QLED panels are similar to other LCD-based panels and do not suffer from issues such as burn-in, which can affect OLED screens (although not all devices using OLED panels suffer from burn-in).
7. QLED TVs Tend to be More Affordable
In my opinion, QLED and OLED displays excel in picture quality, and televisions using these technologies are available in a wide range of large sizes as well as 4K and 8K resolutions.
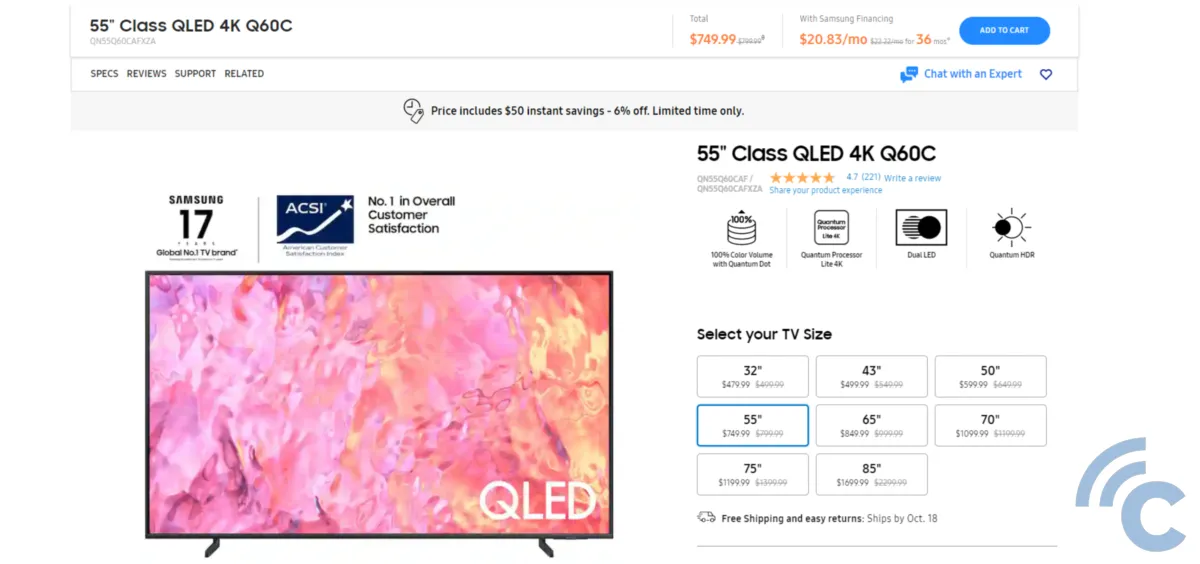
However, if you are looking for a larger-sized television, choosing a QLED TV tends to be a more economical choice. To illustrate, I did a price comparison between QLED and OLED TVs on Samsung's American website. Samsung's QLED monitor with a 55-inch screen (specifically the Q6C model) retails for $749.99. In contrast, the Samsung OLED S95C with a 55-inch screen is listed at $1,899.99.
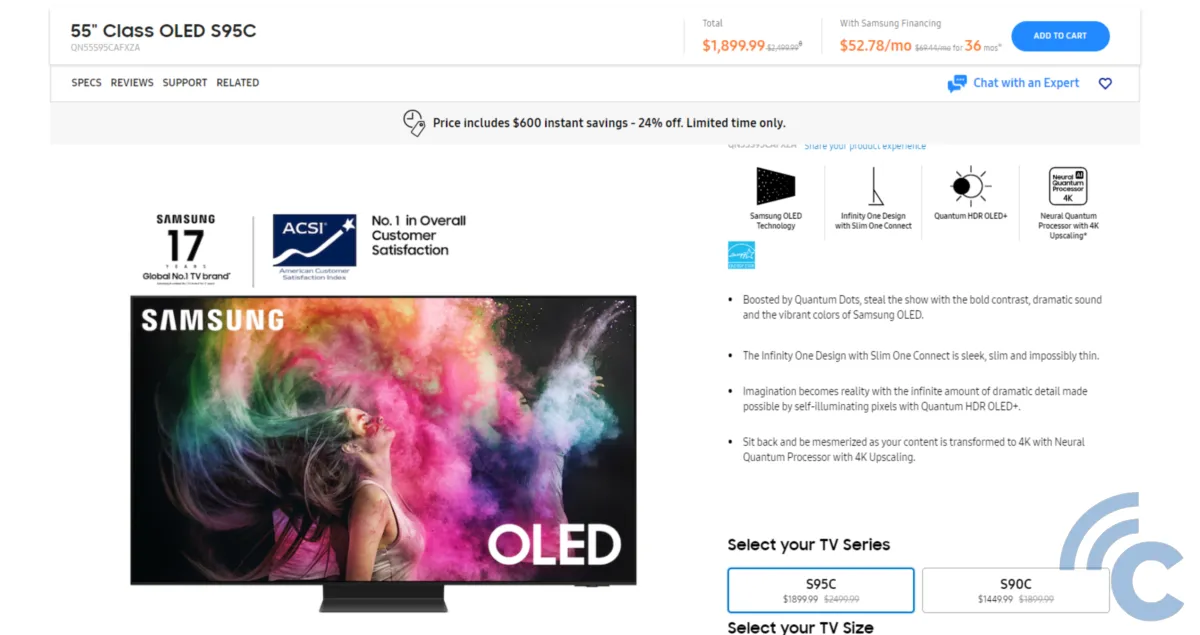
However, this difference is also reasonable considering that OLED panels are the best display panels that can offer sharper and clearer colors.
Summary
Some people may be confused by the term television with a QLED display panel. It is true that it uses LED backlighting. However, QLED is actually a panel from the LCD family. Its working mechanism is quite different from OLED.
However, QLED has improved a lot compared to the previous LCD display panel technology. For content consumption and content creation, QLED screens are sufficient.
Even QLED screens have a relatively lower price than OLED. That way, QLED displays can be an alternative if you want to have a good television or monitor, but are stuck on cost. Hopefully, you now know the difference between QLED and OLED.
