Differences Between IPS, AMOLED, and Super AMOLED
Today, smart devices like smartphones, tablets, computers, laptops, and portable gaming consoles utilize diverse display panel technologies. Among the most prevalent are IPS LCD, AMOLED, and Super AMOLED.
These terms denote the capacity of each screen to offer visual comfort to users. Each type comes with its own set of advantages and drawbacks.
Typically, IPS LCD screens are found on more budget-friendly phones, whereas AMOLED and Super AMOLED screens are associated with higher-end devices.
What are IPS LCD, AMOLED, and Super AMOLED?

IPS LCD, or In-Plane Switching Liquid Crystal Display, employs liquid crystal technology. In this setup, each pixel is composed of a single liquid crystal that serves as the light point. Directly behind this liquid crystal lies a backlight, providing the primary source of illumination.
The emitted light from the backlight then traverses through the liquid crystal layer, undergoing dispersion. The light's emission is subsequently modulated by horizontal and vertical filters flanking the crystal array, allowing certain colors to pass through while blocking others.
The core mechanism of IPS involves sandwiching a liquid crystal layer between two glass sheets. These liquid crystal molecules align parallel to these sheets in a specified orientation. The introduction of IPS LCD technology was primarily to address the limitations in viewing angles and color accuracy encountered with TN (Twisted Nematic) panels.
On the other hand, AMOLED stands for Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode. It's a technology where a series of organic layers, positioned between the anode and cathode layers, emits light.
Given its self-illuminating property, an AMOLED panel doesn't require an additional backlight. Each AMOLED panel consists of an active matrix of OLED pixels, in which once they're electrically activated, these pixels produce light. This is laid atop a TFT layer, and the resulting AMOLED structure includes switches that dictate the current flowing to each individual pixel.
Super AMOLED represents an enhancement introduced by Samsung in 2010. Distinctively, Super AMOLED integrates a touch-responsive component directly into the screen, eliminating the need for a separate top layer.
Difference between IPS, AMOLED, and Super AMOLED
Having defined the terms, let's now explore the differences between IPS, AMOLED, and Super AMOLED display panels.
1. Power Consumption

IPS displays utilize an LED backlight to illuminate the panel. Therefore, even when displaying black, the backlight remains active, consuming more battery power.
In contrast, AMOLED and Super AMOLED panels have the innate ability for each pixel to emit its own light. When rendering black, these pixels simply remain off, conserving energy.
As a result, using dark mode on devices with AMOLED or Super AMOLED screens can significantly enhance battery longevity compared to those with IPS LCDs. According to matob.web.id, AMOLED screens are purportedly up to 10 times more power-efficient than IPS LCDs.
Super AMOLED represents an enhancement of the AMOLED technology, boasting a power efficiency that's approximately 20% greater than its predecessor.
Given their superior power efficiency, only AMOLED and Super AMOLED panels currently support the AOD (Always on Display) feature.
2. Panel Thickness

IPS LCD panels necessitate an internal backlight as their primary light source. In contrast, both AMOLED and Super AMOLED panels allow each pixel to produce its own light. This inherent design difference means that AMOLED and Super AMOLED panels can be thinner, as they don't require the additional backlight layer.
This lack of backlight in AMOLED and Super AMOLED screens also facilitates the integration of under-display fingerprint scanners.
You might observe that smartphones equipped with IPS LCDs don't feature in-display fingerprint sensors. The reason being, the IPS LCD structure doesn't provide sufficient room for such sensors. As a result, phones with IPS LCDs typically position the fingerprint scanner on the rear or the side.
3. Flexibility

The distinction in flexibility between these panels is intrinsically linked to their thickness. Given that AMOLED and Super AMOLED are slimmer, they inherently possess greater adaptability and flexibility.
Flagship and upper-tier smartphones often feature curved screens. This design choice is primarily possible due to the flexibility of AMOLED panels, as curved displays cannot be achieved with IPS LCDs. Many accessories, like smartwatches, also opt for AMOLED screens due to this flexibility.
Furthermore, the flexibility of the AMOLED panel has paved the way for groundbreaking innovations, such as foldable phones and under-display cameras.
4. Color Reproduction
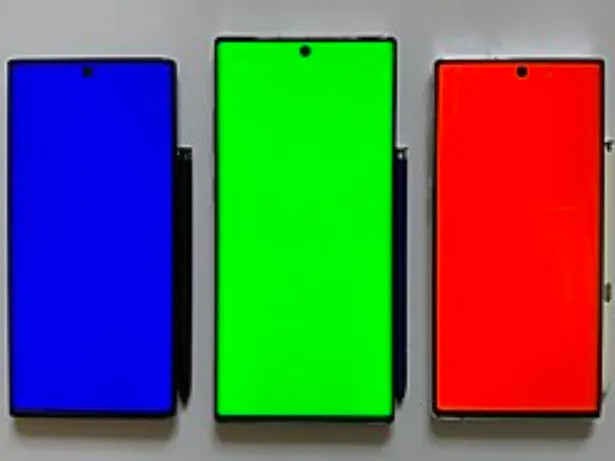
AMOLED and Super AMOLED panels excel when it comes to color representation. Relative to IPS LCDs, both AMOLED variants boast a color gamut that covers 90% of the Adobe RGB spectrum, offering a 20% broader color range than many other display panels.
5. Risk of Burn-In
 Source: Asurion.com
Source: Asurion.comSuper AMOLED and AMOLED panels have certain vulnerabilities when used over extended periods. If static images remain on the screen in the same spot for prolonged durations, they can lead to permanent "shadow" impressions, commonly known as burn-in.
In general, OLED panels, including AMOLED and Super AMOLED, are more prone to this burn-in issue compared to IPS LCDs. For instance, if you play RPG games that have static HUDs continuously for 8 hours a day, you might first notice image retention (a short-term form of burn-in) on AMOLED screens. Over time, this temporary image retention can evolve into permanent burn-in.
6. Contrast Ratio

As previously discussed in the descriptions of each panel type, AMOLED and Super AMOLED panels don't need an internal backlight layer. This is because each pixel is capable of emitting its own light, allowing pixels representing black areas to be completely turned off. This leads to the screen portraying a genuine deep black color, known as "true black".
In contrast, IPS LCDs have a consistent backlight that stays on, causing the black displayed to have a more grayish hue rather than a true black. For instance, the Tecno Camon 19 Pro, equipped with an IPS LCD panel, has a contrast ratio of 1597:1, as cited by GSM Arena. The minimum brightness level it can achieve is 0.3 nits.
Conversely, smartphones with AMOLED panels, such as the Redmi Note 11 and POCO M4 Pro, can achieve a minimum brightness level of 0 nits, and their contrast ratios are effectively infinite.
7. Production Cost
Have you noticed that AMOLED panels are predominantly found in higher-priced smartphones? This is largely due to the fact that the production costs for AMOLED and Super AMOLED are higher than for IPS LCD.
However, with rapid technological advancements, AMOLED panels are now making their way into not just mid-to-high-end phones, but also some entry-level devices. Nonetheless, IPS LCD panels remain the prevalent choice for most entry-level smartphones.
8. Brightness Level

While AMOLED panels are widely recognized for their ability to render sharper and more vibrant colors compared to IPS LCDs, there are also noteworthy distinctions between AMOLED and its advanced counterpart, Super AMOLED.
Super AMOLED boasts several enhancements over standard AMOLED. Notably, Super AMOLED can achieve brightness levels that surpass AMOLED by 20%. Moreover, it has 80% less light reflection. As a result, smartphones equipped with Super AMOLED screens offer improved visibility and comfort for users, especially when viewed outdoors in daylight.
Conclusions
We've delved into the distinctions between the three prominent display panels: IPS LCD, AMOLED, and Super AMOLED. Presently, all three panels have their place in the mobile industry. IPS LCDs offer manufacturers a cost-effective option, ideal for budget-friendly devices.
Conversely, Super AMOLED panels not only provide a more vibrant visual experience but also contribute to significant power savings, allowing devices to last up to 10 times longer on a single battery charge. So, which panel resonates with you, dear Carisinyal reader? We'd love to hear your thoughts in the comment section below.
